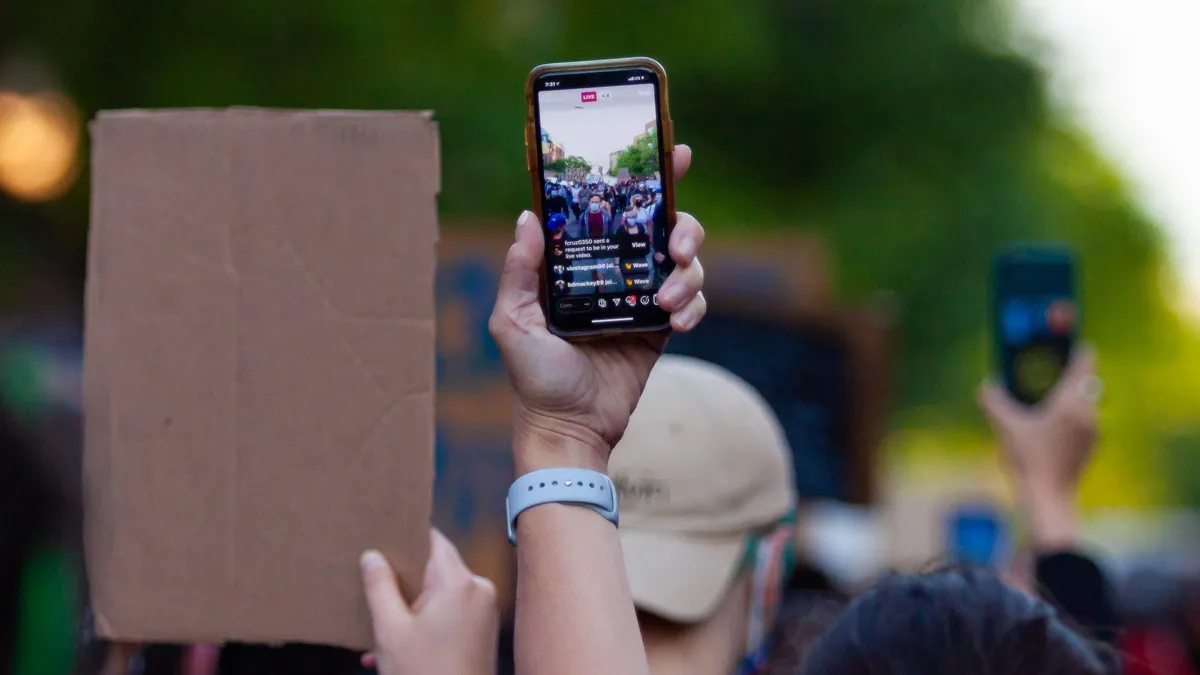
Across the globe, protests against police brutality, institutional racism, and various social injustices are becoming more common. The right to protest is a fundamental constitutional right in many democratic nations, but governments and law enforcement agencies frequently employ extensive surveillance techniques to track and identify demonstrators.
For instance, in 2017, the U.S. Department of Justice attempted to obtain the IP addresses of 1.3 million individuals who visited a website used to coordinate protests against the presidential inauguration. This illustrates how digital footprints can make protesters vulnerable to tracking.
Beyond digital surveillance, authorities can also track individuals using facial recognition software, social media monitoring, and even by confiscating smartphones. Given these threats, it is crucial to take proactive steps to protect your identity and privacy while exercising your right to protest. This guide will outline key privacy measures, offer practical advice, and discuss how to stay safe while standing up for justice.
1. Preparing Before You Protest
A. Minimize Your Digital Footprint
- Avoid Bringing Your Personal Smartphone: If possible, leave your personal smartphone at home and use a burner phone without any personal data.
- Disable Location Services: Turn off GPS, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi to prevent location tracking.
- Use Encrypted Messaging Apps: Communicate with fellow protesters via encrypted platforms like Signal or Telegram.
- Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help mask your IP address and prevent tracking.
B. Dress to Avoid Identification
- Wear Neutral Clothing: Avoid wearing distinct logos, colors, or unique accessories that could make you easily identifiable.
- Cover Your Face: Use a mask, hat, or sunglasses to prevent facial recognition software from identifying you.
- Wear Protective Gear: Goggles, gloves, and long sleeves can protect you from tear gas, pepper spray, and fingerprint tracking.
C. Plan for Legal Safety
- Know Your Rights: Research local laws regarding protests and what law enforcement can and cannot do.
- Have a Lawyer's Contact Information: Memorize or write down the phone number of a lawyer or legal aid organization.
- Avoid Carrying Identifiable Documents: If possible, carry a photocopy of your ID instead of the original.
2. Staying Safe During the Protest
A. Be Mindful of Surveillance
- Avoid Using Biometrics: Disable fingerprint or face unlock on your phone to prevent forced access.
- Beware of Drones and CCTV Cameras: Stick to areas with limited surveillance.
- Turn Off Automatic Photo Tagging: Ensure social media apps do not automatically tag your face in pictures.
B. Be Cautious About Social Media
- Do Not Post Live Updates: Posting in real-time can reveal your location.
- Blur Faces in Shared Photos: Use tools like Signal’s built-in face-blurring feature before sharing images.
- Use Anonymous Accounts: Create a temporary social media account if you must post updates.
C. Stay in Groups and Follow Safety Protocols
- Stay With Trusted People: Avoid wandering alone, as groups provide protection.
- Have an Exit Plan: Identify safe routes to leave if tensions rise.
- Be Prepared for Medical Emergencies: Carry a small first aid kit with essentials like bandages, water, and saline solution.
3. After the Protest: Ensuring Continued Safety
A. Secure Your Digital Information
- Delete Sensitive Messages: Erase messages that could incriminate you or others.
- Clear Browsing History: Remove any web activity related to protest organization.
- Turn Off Your Burner Phone: If you used a temporary phone, turn it off when not in use.
B. Monitor Legal Repercussions
- Check for Legal Updates: Stay informed about any arrests or legal actions against protesters.
- Seek Legal Help if Needed: If you were arrested or harassed, contact a lawyer immediately.
C. Support the Movement
- Share Information Responsibly: Educate others about safe protesting practices.
- Help Detainees: Support those arrested by donating to legal defense funds.
- Continue Advocacy Online: Even after the protest, continue raising awareness about the cause.
How to Hide Your Smartphone's Identity
In an era where digital surveillance is widespread, protecting your smartphone's identity is crucial, especially in situations where personal data might be at risk of seizure. While the simplest way to ensure complete privacy is to avoid carrying a phone altogether, this is often impractical. Communication devices are essential, particularly during emergencies. Additionally, mobile cameras have played a significant role in documenting protests, enabling people worldwide to understand the reasons behind demands for change.
If you are participating in a protest or any event where privacy is a concern, it is vital to take measures to secure your smartphone and minimize exposure to potential tracking or data breaches. Here are some practical steps you can take to enhance your privacy and protect your digital identity:
1. Use a Burner Phone
One of the most effective ways to protect your personal data is to use a burner phone—a cheap, prepaid device that isn’t linked to your personal identity. Here’s how you can maximize its effectiveness:
- Purchase the phone and SIM card with cash to avoid linking the transaction to your identity.
- Do not connect the device to your personal email, social media accounts, or any identifiable services.
- Use it only when necessary and keep it powered off when not in use to avoid location tracking.
2. Disable Unnecessary Connectivity Features
Your smartphone constantly communicates with cell towers, Wi-Fi networks, and Bluetooth devices, which can be used to track your location and identity. To mitigate these risks:
- Turn off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth when not in use, as they can be used for passive tracking.
- Use airplane mode when you don’t need network connectivity.
- Avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi, especially unsecured networks, as they can be exploited to access your data.
3. Use Encrypted Messaging and Calls
Standard calls and SMS messages are not secure and can be intercepted. Instead, use end-to-end encrypted messaging apps such as:
- Signal: Offers encrypted messaging, voice, and video calls.
- Telegram (Secret Chats): Provides self-destructing messages and encryption.
- Session: A decentralized messaging app that requires no phone number.
When using these apps, enable disappearing messages and avoid storing sensitive conversations on your device.
4. Mask Your Phone Number
If you need to make calls but want to keep your identity private, consider:
- Using a Voice over IP (VoIP) service such as Google Voice, ProtonMail’s ProtonVPN with Secure Call, or temporary number services like Burner.
- Avoiding direct calls that can reveal your real phone number.
5. Use a VPN for Internet Browsing
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic, making it harder for third parties to track your online activities. Choose a VPN provider that:
- Has a no-log policy.
- Offers strong encryption and security features.
- Is based in a country with strong privacy protections.
6. Disable Location Tracking
Your phone’s GPS can reveal your exact location. To prevent this:
- Disable location services for all apps unless absolutely necessary.
- Avoid taking photos with location metadata (EXIF data) enabled.
- Regularly review and delete location history stored in Google or Apple services.
7. Use Secure Browsers and Search Engines
Standard web browsers and search engines track user activity. Instead:
- Use privacy-focused browsers like Brave, Tor, or Firefox with enhanced privacy settings.
- Rely on search engines like DuckDuckGo or Startpage that do not track searches.
8. Limit App Permissions
Many apps request unnecessary permissions that can expose your data. To mitigate this risk:
- Review and restrict app permissions in your phone settings.
- Uninstall apps that are not essential.
- Use open-source alternatives to mainstream apps when possible.
9. Avoid Biometric Unlocking
Fingerprint and facial recognition unlock methods can be exploited under coercion. Instead:
- Use a strong alphanumeric password.
- Disable biometric authentication before entering high-risk situations.
10. Be Cautious with Social Media
Even if you take all the precautions on your phone, your online activity can still expose you. To stay anonymous:
- Avoid sharing real-time location updates.
- Use pseudonyms instead of real names.
- Be mindful of metadata in photos and videos before uploading.
11. Secure Your Photos and Videos
If you're documenting events, your media files might contain sensitive information. To protect them:
- Use apps like ObscuraCam to blur faces before sharing images.
- Store files in encrypted storage services.
- Be cautious about sharing footage that could endanger individuals.
12. Regularly Clear Your Data
If your phone is confiscated, even deleted data can sometimes be recovered. To ensure safety:
- Regularly clear call logs, messages, and browsing history.
- Use secure deletion tools that overwrite deleted files.
Using a Secondary Phone for Privacy and Security
Why Consider a Secondary Phone?
In today's digital world, our smartphones hold an enormous amount of personal data, making them a potential risk in situations where privacy and security are crucial. Whether you are attending a protest, traveling to a high-surveillance area, or simply want to keep your primary device safe, using a secondary phone can be a smart move.
Benefits of Using a Separate Phone
- Enhanced Privacy: A secondary phone with minimal applications reduces the chances of data tracking and unauthorized access.
- Reduced Digital Footprint: By limiting apps and personal accounts, you decrease the risk of online monitoring.
- Protection from Confiscation: In events like protests or high-risk travels, a separate phone prevents sensitive data exposure if your primary device is seized.
- Battery and Performance Optimization: A secondary phone ensures that your main device remains charged and available for emergencies.
How to Set Up a Secure Secondary Phone
Setting up a secondary phone requires careful consideration. Below are some key steps:
1. Choose a Suitable Device
If you don’t already have a spare phone, consider getting a basic device with minimal smart features. A simple phone with calling and texting capabilities can be enough for essential communication while keeping your digital presence minimal.
2. Install Only Essential Apps
Avoid installing unnecessary apps that may track your data. Some must-have applications include:
- Encrypted messaging apps (e.g., Signal, Telegram with secret chats)
- Navigation apps that work offline (e.g., OSMAnd, MAPS.ME)
- Secure browsing options (e.g., Tor Browser, DuckDuckGo)
3. Use a Separate SIM Card
Consider purchasing a prepaid or temporary SIM card instead of using your primary number. This helps keep your identity anonymous, especially in situations where personal data protection is important.
4. Disable Unnecessary Features
To prevent tracking and unwanted surveillance, turn off the following features when they are not needed:
- Location Services: Disable GPS tracking to avoid being pinpointed.
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: Keep them off when not in use to prevent unauthorized access.
- Auto-Syncing: Stop automatic data backups to prevent syncing your activity with cloud accounts.
5. Log Out of Personal Accounts
Ensure that you do not log into personal email, social media, or banking apps on this phone. The less personal information stored, the better protected you are.
6. Encrypt Your Data
If the phone has storage encryption options, enable them to add an extra layer of security. This prevents unauthorized access even if the device is lost or seized.
Alternative Measures If You Cannot Use a Secondary Phone
Not everyone has access to a second phone, but you can still take steps to protect your primary device:
- Remove Unnecessary Apps: Temporarily uninstall apps that store personal information.
- Use a Secure Mode: Some phones offer a guest mode or secondary profile that can be used as a temporary secure environment.
- Turn Off Tracking Features: Ensure that location, Bluetooth, and unnecessary syncing services are disabled.
- Log Out of All Accounts: Sign out of social media, email, and cloud storage accounts before heading into situations that require extra security.
Additional Security Tips
Aside from using a secondary phone, here are some extra precautions to ensure your data remains safe:
1. Use Strong Authentication
Set up a strong PIN or password instead of fingerprint or facial recognition, as biometric data can sometimes be forced or bypassed.
2. Regularly Clear Data
Periodically delete sensitive messages, call logs, and browsing history to reduce stored data risks.
3. Keep Your Software Updated
Ensure that your device has the latest security updates to protect against vulnerabilities.
4. Use Disposable Communication Methods
If engaging in sensitive conversations, consider using temporary email addresses and burner phone numbers.
5. Be Aware of Network Monitoring
Avoid connecting to public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks, as they can be used to intercept data transmissions.
Secure Communication During Protests: Protecting Your Privacy
Effective communication is paramount during any protest. It allows for coordination, information sharing, and ensuring the safety of all participants. In situations where surveillance or monitoring is a concern, safeguarding your communication channels becomes even more critical. This means choosing tools and methods that prioritize privacy and security.
Choosing the Right Messaging App
Not all messaging applications are created equal when it comes to privacy. Some offer features that significantly enhance your security, while others leave your communications vulnerable.
Key Considerations for Secure Messaging:
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): This is a fundamental requirement. E2EE ensures that only the sender and recipient can read the messages. Not even the messaging service provider can access the content.
- Open-Source Code: Open-source apps allow security experts to scrutinize the code for vulnerabilities, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Minimal Data Collection: Opt for apps that collect minimal user data. Ideally, they should not store metadata like who you're talking to or when.
- Disappearing Messages: This feature allows you to set messages to automatically delete after a certain period, reducing the risk of them falling into the wrong hands.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for an extra layer of security, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access your account.
Recommended Secure Messaging Apps:
- Signal: Widely regarded as one of the most secure messaging apps. It offers E2EE by default, is open-source, and collects minimal data.
- Threema: A paid app that prioritizes privacy. It offers E2EE, doesn't require a phone number or email to register, and is open-source.
- Session: This is an end-to-end encrypted messaging application that minimizes sensitive metadata, and routes all messages through a decentralized server network. Session is also open source.
- Wickr: Offers E2EE, ephemeral messaging, and secure file sharing.
While WhatsApp offers end-to-end encryption, it's owned by Meta (formerly Facebook), which has a history of data collection practices. This raises concerns about potential metadata collection.
Beyond Messaging Apps: Physical Security Measures
In addition to secure messaging, consider these physical security measures:
Faraday Bags: Blocking Location Tracking
A Faraday bag is a simple yet effective tool for blocking electromagnetic signals, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and GPS. By placing your phone inside a Faraday bag, you prevent it from transmitting or receiving signals, effectively making it invisible to location tracking. However, it is also important to remember that if any bluetooth devices or trackers are on your person, a faraday bag may not block those from revealing a location.
Practical Tips for Using Faraday Bags:
- Choose the right size: Ensure the bag is large enough to comfortably fit your phone and any other devices you want to shield.
- Test the bag: Before relying on it, test the bag's effectiveness by trying to make a call or connect to Wi-Fi while your phone is inside.
- Keep it sealed: Ensure the bag is properly sealed to prevent signal leakage.
- Consider a Faraday pouch for keys: New vehicles may have key fobs that transmit data, and can be vulnerable to theft or surveillance.
Alternative ways to mitigate tracking.
- Turn off location services: Disable GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth when not needed.
- Use a burner phone: A prepaid phone with minimal personal information linked to it can be used for sensitive communications.
- Remove your SIM card and battery: Physically removing these components can prevent your phone from transmitting signals. (Please note that some modern phones do not allow for the user to remove the battery)
Digital Hygiene Practices
Protecting your privacy during protests extends beyond just using secure messaging apps and Faraday bags. Here are some essential digital hygiene practices:
Secure Your Devices:
- Use strong, unique passwords: Employ a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
- Enable full disk encryption: Encrypt your device's storage to protect your data in case it's lost or stolen.
- Keep your software updated: Install the latest security updates for your operating system and apps.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address, enhancing your online privacy.
Be Mindful of What You Share Online:
- Avoid posting sensitive information on social media: This includes your location, plans, and personal details.
- Be cautious about sharing photos and videos: Metadata in images and videos can reveal your location and other information.
- Use privacy-focused browsers and search engines: Consider browsers like Tor or Brave, and search engines like DuckDuckGo.
Threat Modeling
Understand potential threats. This will allow the user to properly assess the risk, and prepare security measures based on likely threats. For example, are you more worried about local law enforcement, or national agencies? This will change the needed level of security. If you are extremely concerned about state level actors, it may be worth it to seek out a security professional.
Physical security during protests
While this article has focused on digital safety, physical safety is also important during protests. Be aware of your surroundings, stay with a group, have an emergency contact, and make an escape plan.
By implementing these security measures and practicing good digital hygiene, you can significantly enhance your privacy and safety during protests.
Protecting Your Digital Data: Essential Security Measures for Your Smartphone
In today's digitally driven world, our smartphones hold a vast amount of sensitive personal data. From private conversations and financial information to personal photos and location history, our devices are a treasure trove of information that could be misused if it falls into the wrong hands. Therefore, safeguarding this data is paramount, especially in situations where your device might be confiscated or accessed without your consent.
Data Encryption: Your First Line of Defense
One of the most effective ways to protect your data is through encryption. Encryption essentially scrambles your data, rendering it unreadable without a decryption key, which is typically your passcode or password. This means that even if someone gains physical access to your phone, they won't be able to access your information without the correct credentials.
How to Encrypt Your Android Device:
Most modern Android devices offer built-in encryption capabilities. Here's how to enable it:
- Navigate to your phone's Settings.
- Scroll down and tap on Security (or similar, depending on your device's manufacturer).
- Look for the option labeled Encrypt phone or Encrypt storage.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the encryption process.
Important Considerations:
- The encryption process can take some time, depending on the amount of data stored on your device.
- Ensure your phone is fully charged or plugged into a power source before starting the encryption process. Interrupting the process can lead to data corruption.
- Once encrypted, your data can only be accessed with your passcode or password. Therefore, choose a strong and memorable passcode that you won't forget.
iOS Encryption:
Apple devices, specifically iPhones, have automatic encryption enabled by default when you set a passcode. This is a significant advantage, as it simplifies the process for users. However, it's crucial to understand that the strength of this encryption is directly tied to the strength of your passcode.
The Importance of a Strong Passcode
Your passcode is the key to unlocking your encrypted data. Therefore, choosing a strong and unique passcode is essential. Avoid easily guessable passcodes like "1234" or "password." Instead, opt for a complex combination of letters, numbers, and symbols.
Why Biometric Authentication Can Be a Security Risk:
While convenient, biometric authentication methods like fingerprint and facial recognition can be a security liability. In many jurisdictions, law enforcement can compel you to unlock your phone using your biometrics. This is because biometrics are considered physical characteristics, unlike passcodes, which are considered knowledge-based.
Practical Advice:
- Disable biometric unlock features on your phone, especially in situations where you anticipate potential security risks.
- Rely solely on a strong alphanumeric passcode for unlocking your device.
- Consider using a passphrase instead of a traditional passcode. Passphrases are longer and more complex, making them significantly harder to crack.
Securing Individual Applications
In addition to device-level encryption, many applications offer their own security features, allowing you to add an extra layer of protection to your sensitive data. Secure messaging apps, for example, often provide options for password-protecting your conversations.
Example: Secure Messaging Apps
Apps like Signal and Telegram offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring that only the sender and recipient can read the messages. Some of these apps also allow you to set a separate passcode for the app itself, adding an extra layer of security.
Practical Advice:
- Explore the security settings of your frequently used apps and enable any available security features.
- Be cautious about granting apps excessive permissions. Only allow necessary permissions to minimize potential security risks.
Additional Security Measures
Beyond encryption and strong passcodes, consider implementing these additional security measures:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA on your online accounts whenever possible. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your phone's operating system and apps updated to patch security vulnerabilities and ensure you have the latest security features.
- Remote Wipe Capabilities: Familiarize yourself with your device's remote wipe capabilities. This allows you to erase all data on your phone remotely if it is lost or stolen.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Use a VPN, especially on public Wi-Fi networks, to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your online activity from prying eyes.
- Limit Data Storage: Be mindful of the data you store on your phone. Avoid storing highly sensitive information unless absolutely necessary.
- Backup your information: Frequently backup the most important data from your phone to a secure location.
Understanding the Legal Landscape
It's important to be aware of the legal landscape surrounding data privacy and law enforcement access to your digital devices. Laws and regulations vary significantly between jurisdictions. Familiarize yourself with the laws in your region to understand your rights and responsibilities.
Key Considerations:
- In some jurisdictions, law enforcement may be able to compel you to provide your passcode or unlock your device.
- Refusing to comply with a lawful order could have legal consequences.
- Consult with a legal professional to understand your rights and options in specific situations.
Staying Informed and Proactive
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, with new security threats emerging regularly. Stay informed about the latest security best practices and take a proactive approach to protecting your data. By implementing the measures outlined in this discussion, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of data breaches or unauthorized access to your personal information.
In today's interconnected world, protecting your online privacy is more crucial than ever. One of the fundamental ways your online activity can be traced is through your IP address. This unique identifier reveals your approximate location and can be used to monitor your browsing habits. While GPS location tracking is a well-known concern, IP address tracking poses a significant threat to your privacy, especially when connected to local networks.
The Limitations of Simply Avoiding Local Networks
One might think that avoiding local networks altogether would solve the problem. However, this is often impractical. Many of our daily activities rely on internet connectivity, and disconnecting entirely isn't a realistic solution. Moreover, even if you consciously try to avoid local networks, a simple lapse in vigilance, such as forgetting to disable Wi-Fi, can expose your IP address.
The Solution: Leveraging a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A more robust and reliable method for preventing IP tracking is to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server, effectively masking your real IP address and routing your internet traffic through the VPN server.
How a VPN Conceals Your IP Address
When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic appears to originate from the VPN server's location rather than your actual location. For example, if you are located in the United States and connect to a VPN server in Canada, websites and online services will perceive your location as being in Canada. This ability to spoof your location provides a significant layer of anonymity, making it considerably more challenging for anyone to track your online activities.
Encryption: Protecting Your Browsing Data
In addition to masking your IP address, a VPN encrypts your browsing data. This encryption scrambles your data, rendering it unreadable to anyone intercepting it. This ensures that even if your data is intercepted, it remains indecipherable, safeguarding your sensitive information from prying eyes.
Practical Advice for VPN Usage
- Choose a reputable VPN provider: Not all VPNs are created equal. Opt for a reputable provider with a strong track record of protecting user privacy. Look for VPNs that offer robust encryption protocols, a strict no-logs policy, and a wide range of server locations.
- Select a server close to your actual location (for speed): While you can connect to servers worldwide, choosing one that's geographically close to your location often provides better performance and faster speeds.
- Enable the kill switch: Most VPNs offer a kill switch feature, which automatically disconnects your internet connection if the VPN connection drops. This prevents your actual IP address from being exposed in case of a VPN outage.
- Use a VPN on all your devices: Ensure that your VPN is installed and active on all your devices, including your computer, smartphone, and tablet, to maintain consistent protection.
- Consider using a VPN router: For comprehensive protection of all devices on your home network, consider setting up a VPN router. This will route all traffic through the VPN, eliminating the need to install VPN software on individual devices.
- Understand the VPN's no-logs policy: Prioritize a vpn that has an audited and verified no logs policy. This ensures that the VPN provider is not keeping records of your online activity.
- Be aware of free VPN limitations: While free VPNs may seem tempting, they often come with limitations, such as slower speeds, limited server locations, and potential data logging. Free VPNs may also display intrusive ads or even sell your data to third parties.
- Keep your VPN software up to date: Regularly update your VPN software to ensure you have the latest security patches and features.
Beyond IP Masking: Additional Benefits of Using a VPN
- Bypassing geo-restrictions: VPNs allow you to access content that may be restricted in your region, such as streaming services or websites.
- Protecting against ISP throttling: Internet service providers (ISPs) sometimes throttle bandwidth for specific types of traffic, such as streaming or torrenting. A VPN can help prevent this by encrypting your traffic, making it difficult for ISPs to identify and throttle it.
- Securing public Wi-Fi connections: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them vulnerable to hacking and data interception. A VPN encrypts your connection, protecting your data even on unsecured networks.
- Enhanced privacy from online trackers: VPNs help prevent websites and online services from tracking your browsing habits and collecting your personal information.
- Protection from targeted advertising: By masking your IP address and encrypting your data, VPNs can limit the effectiveness of targeted advertising.
Understanding the Nuances of IP Tracking
It's important to understand that IP address tracking is just one piece of the broader online tracking puzzle. Other methods, such as cookies, browser fingerprinting, and device tracking, can also be used to monitor your online activities. While a VPN can significantly enhance your privacy, it's not a silver bullet. Combining a VPN with other privacy-enhancing tools and practices is essential for comprehensive online protection.
Additional Tools and Practices for Enhanced Privacy
- Use a privacy-focused browser: Consider using a browser like Tor or Brave, which are designed to prioritize user privacy.
- Install privacy-enhancing browser extensions: Browser extensions like Privacy Badger and uBlock Origin can block trackers and intrusive ads.
- Regularly clear your browsing data: Clearing your browsing history, cookies, and cache can help limit the amount of information websites can collect about you.
- Use strong, unique passwords: Employ a password manager to generate and store strong, unique passwords for your online accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from your smartphone.
- Review and adjust your privacy settings: Regularly review and adjust the privacy settings on your devices, browsers, and online accounts.
- Be mindful of the information you share online: Exercise caution when sharing personal information online, especially on social media and public forums.
By understanding the risks of IP tracking and implementing a combination of these privacy-enhancing measures, you can take control of your online privacy and safeguard your sensitive information from prying eyes.
Social Media as a Double-Edged Sword: Protecting Yourself in the Digital Age
Social media has become an integral part of modern communication, facilitating the rapid dissemination of information and enabling global connectivity. However, this same power can be weaponized against individuals, particularly in contexts like protests and activism. Understanding the risks and implementing precautionary measures is crucial for safeguarding your privacy and security.
The Dangers of Digital Footprints
Your social media presence, encompassing platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, leaves a digital trail that can easily identify you. This is especially pertinent when coordinating or participating in events like protests, where authorities or opposing groups may seek to identify individuals. Simply being logged into your social media accounts on your phone can compromise your anonymity, as it provides a direct link between the device and your identity.
Practical Advice:
- Consider temporarily deleting social media apps or logging out of your accounts on your phone before attending any potentially sensitive event.
- Use a separate, "burner" device for communication and social media during protests, if possible.
- Enable two-factor authentication on all your accounts for an extra layer of security.
- Regularly review and adjust your privacy settings to limit the information shared publicly.
Sharing Content Responsibly
The desire to share images and videos from protests is understandable, as it can amplify the message and raise awareness. However, indiscriminately posting such content can inadvertently endanger yourself and others. Protecting the privacy of fellow participants is paramount. Blurring faces or omitting identifying details can prevent individuals from being recognized.
Furthermore, be mindful of the content you share and its potential implications. Even seemingly innocuous posts can be misinterpreted or used against you. Authorities might analyze your posts to identify other participants or gather evidence. Remember, you are not only putting yourself at risk but also potentially endangering others.
Expanded Insights:
- Metadata Removal: Before sharing any photo or video, remove the metadata. This data can contain location information, timestamps, and device details, which could be used to identify you. Numerous free tools are available online for metadata removal.
- Content Moderation: Be selective about the content you consume and share. Misinformation and propaganda often circulate during protests. Verify information from multiple reliable sources before reposting.
- Language and Tone: Exercise caution in the language and tone used in your social media posts. Avoid inflammatory or threatening language that could be misinterpreted or used to incriminate you.
- Platform Specifics: Understand the privacy policies and settings of each social media platform. Some platforms have stricter data collection and sharing practices than others.
- Future Implications: Consider the long-term consequences of your posts. Content shared online can persist indefinitely, potentially impacting your future employment or personal life.
The Nuclear Option: Deleting Your Accounts
For those seeking maximum anonymity, deleting social media accounts may be the most prudent course of action. Platforms like Facebook and WhatsApp collect vast amounts of data about their users, creating detailed profiles that can be accessed by various entities. If you prefer to err on the side of caution, consider deleting your accounts, particularly before engaging in activities where your identity could be compromised.
Practical Advice:
- Back up any essential data, such as photos or contacts, before deleting your accounts.
- Utilize secure messaging apps like Signal or Telegram, which offer end-to-end encryption for enhanced privacy.
- If complete deletion is not feasible, deactivate your accounts temporarily and clear your browsing history and cookies.
- Review third-party app access to your social media accounts and revoke permissions as needed.
- Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to mask your IP address and encrypt your internet traffic, adding another layer of security.
Beyond Social Media: Comprehensive Security Measures
Protecting yourself goes beyond social media. Adopt a holistic approach to security that encompasses various aspects of your digital and physical life.
Additional Security Measures:
- Physical Security: Be aware of your surroundings and avoid sharing personal information with strangers. Consider using a burner phone number for contact tracing or event registration.
- Device Security: Use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and devices. Enable biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, for added security. Keep your software and apps updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data on your devices and in cloud storage. Use encrypted messaging and email services.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Educate yourself about common cybersecurity threats, such as phishing and malware. Be cautious about clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
- Legal Considerations: Familiarize yourself with the laws and regulations regarding online activity and privacy in your jurisdiction.
- Digital Detox: Periodically disconnect from social media and digital devices to reduce your exposure to potential risks.
- Community Support: Collaborate with like-minded individuals and organizations to share information and resources on digital security.
In conclusion, social media offers unparalleled opportunities for communication and mobilization, but it also presents significant risks. By understanding these risks and taking proactive measures, you can protect yourself and others in the digital age.
In today's increasingly surveilled world, protecting your privacy and anonymity is paramount. Law enforcement agencies and other entities employ a wide range of surveillance technologies that extend far beyond simply tracking your phone or social media activity. To safeguard yourself, it's crucial to understand these technologies and implement practical countermeasures.
Understanding Surveillance Technologies
Here's a breakdown of some common surveillance methods:
- Facial Recognition: This technology analyzes facial features to identify individuals from digital images or video footage. It's increasingly used in public spaces, by law enforcement, and even in retail settings.
- Surveillance Cameras: High-resolution cameras are ubiquitous in urban environments, capturing footage that can be used to track movements and identify individuals. Advanced systems often integrate with facial recognition software.
- Location Tracking: Beyond your phone's GPS, various methods can pinpoint your location, including license plate readers, Wi-Fi tracking, and cell tower triangulation.
- Biometric Data Collection: This involves gathering unique biological data such as fingerprints, iris scans, and even gait patterns, which can be used for identification.
- Online Monitoring: Your online activity leaves a digital trail that can be tracked and analyzed. This includes your browsing history, social media posts, and online purchases.
- Data Brokers: Companies that collect and sell personal information, often without individuals' knowledge or consent, creating detailed profiles that can be used for surveillance purposes.
Practical Steps to Protect Yourself
Here are actionable strategies to enhance your personal security and reduce your vulnerability to surveillance:
Physical Anonymity
- Dress inconspicuously: Opt for clothing in neutral colors that blend in with your surroundings. Avoid bright, distinctive patterns or logos that could make you stand out.
- Conceal identifying features: Cover tattoos, piercings, and other unique physical characteristics that could aid in identification.
- Use face coverings: Wearing a face mask not only provides protection against viruses but also obscures your facial features from facial recognition systems.
- Wear sunglasses: Sunglasses can help conceal your eyes, which are a key component of facial recognition. Choose larger frames for better coverage.
- Vary your appearance: Changing your hairstyle, wearing hats or scarves, or even altering your gait can make it more difficult to be identified consistently.
Digital Privacy
- Limit online information: Minimize the amount of personal information you share online, especially on social media. Review and adjust your privacy settings to restrict access to your data.
- Use privacy-focused browsers and search engines: Consider browsers like Tor or Brave, and search engines like DuckDuckGo, which prioritize user privacy and minimize data collection.
- Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address, making it harder to track your online activity.
- Be cautious with public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing sensitive information on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, as they can be vulnerable to eavesdropping. Use a VPN if you must use public Wi-Fi.
- Review app permissions: Regularly check the permissions granted to apps on your devices and revoke any unnecessary access to your data.
- Use encrypted communication: Opt for encrypted messaging apps like Signal or WhatsApp (with end-to-end encryption enabled) for secure communication.
- Manage your online presence: Regularly search for your name online and take steps to remove or suppress any unwanted or outdated information.
- Utilize password managers: Use a reputable password manager to generate and securely store strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security to your online accounts by enabling 2FA, which requires a second form of verification, such as a code from your phone.
Situational Awareness
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to surveillance cameras, license plate readers, and other potential surveillance technologies in your environment.
- Vary your routines: Avoid predictable patterns in your daily movements, as this can make it easier to track you.
- Use cash for purchases: When possible, use cash instead of credit or debit cards to minimize the digital trail associated with your purchases.
- Secure your devices: Use strong passwords or biometric authentication to protect your devices from unauthorized access. Keep your software updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Be mindful of location data: Disable location services on your devices when not needed, and be cautious about apps that request access to your location data.
Countering Online Harassment and Doxing
In addition to physical and digital security measures, it's essential to be prepared for potential online harassment and doxing, which involves the public release of private information.
- Limit personal information shared online: Be selective about the information you share on social media and other online platforms.
- Use strong privacy settings: Review and adjust your privacy settings on social media and other online platforms to control who can see your information.
- Monitor your online presence: Regularly search for your name online and set up alerts for any new mentions.
- Report harassment and doxing: If you experience online harassment or doxing, report it to the platform where it occurred and consider contacting law enforcement.
- Document everything: Keep records of any online harassment or doxing incidents, including screenshots, timestamps, and URLs.
- Seek support: Reach out to trusted friends, family members, or support organizations for assistance and guidance.
Protecting yourself from surveillance requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses physical anonymity, digital privacy, situational awareness, and proactive measures to counter online harassment. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly enhance your personal security and safeguard your privacy in an increasingly surveilled world.
Staying Vigilant: A Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Identity in the Digital Age
In today's interconnected world, safeguarding your identity is paramount. While implementing various measures can significantly reduce the risk of being tracked or identified, it's crucial to acknowledge that these are not foolproof solutions. True security stems from a vigilant approach, both online and offline. The landscape of surveillance technology is constantly evolving, necessitating a proactive and adaptable strategy.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Before diving into practical advice, it's essential to understand the various threats that can compromise your identity. These threats can range from simple data breaches to sophisticated surveillance techniques. Some common threats include:
- Data Breaches: These incidents involve unauthorized access to sensitive information stored by companies or organizations.
- Phishing Attacks: These deceptive tactics aim to trick individuals into revealing personal information, such as passwords or credit card details.
- Malware and Spyware: Malicious software can infiltrate your devices, monitor your activities, and steal sensitive data.
- Social Engineering: This involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise their security.
- Surveillance Technologies: These include facial recognition, location tracking, and other methods used to monitor individuals' movements and activities.
Practical Advice for Enhancing Your Security
To mitigate these risks, consider the following practical advice:
Online Security Measures
- Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Employ strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts and enable 2FA whenever possible. Consider using a reputable password manager to generate and store your passwords securely.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Use a VPN to encrypt your internet traffic, mask your IP address, and protect your online activities from prying eyes.
- Secure Browsing Practices: Be cautious about the websites you visit and the links you click. Avoid downloading files from untrusted sources and keep your browser up to date.
- Email Security: Be wary of suspicious emails and avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown senders. Use a secure email provider and enable spam filters.
- Social Media Privacy: Review your social media privacy settings and limit the amount of personal information you share online. Be mindful of the content you post and the people you connect with.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating system, applications, and antivirus software up to date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Privacy-Focused Search Engines: Opt for search engines that prioritize user privacy and don't track your search history.
- Minimize Your Digital Footprint: Be mindful of the information you share online, as it can be aggregated and used to create a profile of you. Regularly review and delete any unnecessary or outdated online accounts.
Offline Security Measures
- Physical Security: Protect your physical devices, such as laptops and smartphones, with strong passwords or biometrics. Be cautious about leaving your devices unattended in public places.
- Financial Security: Monitor your bank accounts and credit card statements regularly for any suspicious activity. Be cautious about sharing your financial information online or over the phone.
- Identity Theft Protection: Consider subscribing to an identity theft protection service that monitors your credit report and alerts you to any suspicious activity.
- Be Mindful of Your Surroundings: Be aware of your surroundings and avoid sharing personal information with strangers. Be cautious about discussing sensitive topics in public places.
- Shred Sensitive Documents: Shred any documents containing sensitive information, such as bank statements or credit card bills, before discarding them.
The Importance of Ongoing Vigilance
In addition to these measures, it's crucial to stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices. Follow reputable security blogs and news sources to stay up to date on the latest trends and vulnerabilities. Additionally, be skeptical of any requests for personal information, whether online or offline. If something seems too good to be true, it probably is.
The Role of Technology and Policy
Technology plays a dual role in security. While it can be used to enhance security, it can also be used for surveillance and tracking. It's essential to be aware of the technologies that are being used to monitor individuals and to advocate for policies that protect privacy and civil liberties. Governments and organizations must strike a balance between security and privacy, ensuring that surveillance technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
Building a Culture of Security
Ultimately, security is a shared responsibility. We all have a role to play in protecting our own identities and the identities of others. By staying vigilant, adopting secure practices, and advocating for policies that protect privacy, we can create a more secure and equitable digital world.
In conclusion, while no single solution can guarantee complete protection, a combination of online and offline security measures, coupled with a vigilant approach, can significantly reduce the risk of being identified or tracked. By staying informed, adopting secure practices, and advocating for privacy, we can navigate the digital age with greater confidence and security.




























0 Comments