In a significant step toward aligning state law with constitutional protections, the Texas House voted on May 16, 2025, to preliminarily approve House Bill 1738, which seeks to repeal the state's outdated and unenforceable ban on "homosexual conduct." This legislative move, passing with a 72-55 vote, marks a pivotal moment in Texas' ongoing struggle to reconcile its legal framework with evolving societal values and judicial mandates. This article delves deeply into the historical context, legal implications, societal impact, and political dynamics surrounding the repeal effort, exploring hidden truths, relevant research, and the broader significance of this legislative action.
Historical Context: The Legacy of Texas' Homosexual Conduct Ban
Origins of the 1973 Law
The Texas statute banning "deviate sexual intercourse with another individual of the same sex" was enacted in 1973, reflecting the prevailing social and political attitudes of the time. Rooted in a broader cultural discomfort with homosexuality, the law criminalized consensual same-sex sexual activity, imposing penalties that could include fines and imprisonment. This statute was not unique to Texas; similar "sodomy laws" existed across the United States, often justified by moral or religious arguments.
Research from the Williams Institute at UCLA School of Law indicates that such laws were frequently used to marginalize and discriminate against LGBTQ+ individuals, fostering a climate of fear and stigmatization. In Texas, the law reinforced systemic biases, affecting employment, housing, and social acceptance for gay and lesbian individuals.
The Landmark Lawrence v. Texas Decision
The turning point came in 2003 with the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling in Lawrence v. Texas. This case, originating from a 1998 arrest of two men in Houston for engaging in consensual sexual activity, challenged the constitutionality of Texas' sodomy law. In a 6-3 decision, the Court struck down the law, declaring it a violation of the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. Justice Anthony Kennedy's majority opinion emphasized the right to privacy and individual liberty, stating:
The petitioners are entitled to respect for their private lives. The State cannot demean their existence or control their destiny by making their private sexual conduct a crime.
This ruling not only invalidated Texas' law but also nullified similar statutes in 13 other states, marking a watershed moment for LGBTQ+ rights. However, the Texas statute remained on the books, unenforceable but symbolically significant.
Legislative Efforts to Repeal the Ban
Early Attempts and Persistent Challenges
Efforts to repeal the homosexual conduct ban began shortly after the Lawrence decision, with advocates arguing that retaining an unconstitutional law perpetuated discrimination. Rep. Venton Jones, a Dallas Democrat and one of the first openly Black gay members of the Texas House, noted that the fight to repeal the law has spanned decades, dating back to the 1980s. These efforts faced significant resistance, particularly in a state with a strong conservative legislative majority.
Previous attempts to pass repeal legislation, such as in the 2023 session, faltered due to procedural deadlines and political opposition. The 2025 vote, however, represents a breakthrough, with 12 Republicans joining Democrats to support House Bill 1738. This bipartisan support underscores a shifting political landscape, though challenges remain as the bill moves to the Senate.
The 2025 Vote: A Symbolic Victory
The Texas House's preliminary approval of House Bill 1738 on May 16, 2025, was a historic moment. The vote, which saw a coalition of liberal and conservative lawmakers unite, reflects a growing recognition that outdated laws have no place in a state committed to individual liberty. Rep. Jones, the bill's author, framed the repeal as a matter of fundamental civil liberties, stating on the House floor:
I'm asking you to vote for a law that upholds the principles that Texans should have the freedom and ability to make their own private decisions without unwarranted government interference.
The bill's passage through the House is a testament to the perseverance of advocates who have worked tirelessly to dismantle legal relics of discrimination. However, its fate in the Senate remains uncertain, given the legislative session's impending end on June 2, 2025, and the chamber's more conservative composition.
Political Dynamics: An Unlikely Alliance
Bipartisan Support and Conservative Backing
One of the most striking aspects of the 2025 vote was the bipartisan coalition it forged. Rep. Brian Harrison, a conservative Republican known for his hardline stances, co-authored the bill, arguing that criminalizing homosexuality exceeds the proper role of government. Harrison's support, along with endorsements from figures like U.S. Sen. Ted Cruz and Supreme Court Justice Clarence Thomas, highlights a libertarian strain within conservatism that prioritizes limited government over moral regulation.
Harrison's statement encapsulates this perspective:
Criminalizing homosexuality is not the role of government, and I support repealing it. I will continue consistently fighting for limited government and individual liberty.
This alliance between progressive advocates like Jones and conservative libertarians like Harrison reveals a complex political landscape where ideological principles can sometimes transcend traditional partisan divides.
Opposition and Remaining Hurdles
Despite the bipartisan support, the bill faced opposition from 55 House members, primarily Republicans, who voted against the repeal. The reasons for opposition vary, ranging from moral objections to concerns about political backlash from conservative constituents. In the Senate, where conservative voices hold greater sway, the bill is likely to encounter significant resistance. The tight legislative timeline further complicates its prospects, as senators juggle a flood of competing priorities.
Research from the Pew Research Center indicates that while public support for LGBTQ+ rights has grown significantly—70% of Americans supported same-sex marriage in 2020—pockets of resistance remain, particularly in conservative strongholds like Texas. This dynamic suggests that the repeal effort, while symbolically potent, may face an uphill battle in achieving final passage.
Legal and Social Implications
The Danger of "Zombie Laws"
The retention of unenforceable laws, often termed "zombie laws," poses significant risks. The 2022 Supreme Court decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization, which overturned Roe v. Wade, demonstrated how dormant statutes can be revived. In Texas, Attorney General Ken Paxton attempted to enforce a pre-Roe abortion statute, leading to legal confusion and litigation. This precedent has heightened the urgency of repealing the homosexual conduct ban, as Rep. Jones noted:
It was already past time to do this, and now even more so.
Legal scholars, such as those at the University of Texas School of Law, argue that zombie laws create uncertainty and undermine public trust in the legal system. By removing the homosexual conduct ban, Texas can affirm its commitment to constitutional principles and prevent potential misuse of outdated statutes.
Societal Impact: Beyond Symbolism
While repealing an unenforceable law may seem symbolic, its impact extends far beyond the legal realm. For LGBTQ+ Texans, the presence of the ban in state statutes serves as a constant reminder of historical discrimination. Studies from the Trevor Project show that discriminatory laws and policies contribute to higher rates of mental health challenges among LGBTQ+ youth, including anxiety and depression.
Rep. Jones, reflecting on his experience as a gay man, highlighted the personal significance of the repeal effort:
As a gay man, knowing this law was on the books, even unenforceable, was a reminder of the state’s long-held position of discrimination against people like me.
The repeal effort thus carries profound emotional and cultural weight, signaling to LGBTQ+ individuals that their rights and dignity are valued. It also aligns Texas with broader national trends toward inclusivity, as evidenced by the legalization of same-sex marriage in 2015 and increasing corporate and institutional support for LGBTQ+ rights.
Hidden Truths and Broader Context
The Role of Advocacy and Grassroots Movements
The progress toward repeal would not have been possible without decades of advocacy from LGBTQ+ organizations, such as Equality Texas and the Human Rights Campaign. These groups have worked tirelessly to educate lawmakers, mobilize public support, and challenge discriminatory policies. Their efforts have been bolstered by broader cultural shifts, including increased visibility of LGBTQ+ individuals in media, politics, and public life.
Grassroots activism has also played a critical role. For example, the 2019 "All Means All" campaign by Equality Texas rallied thousands of Texans to advocate for inclusive policies, including the repeal of the homosexual conduct ban. Such movements underscore the power of collective action in driving legislative change.
Intersectionality and Representation
Rep. Jones' identity as a Black gay man adds an intersectional dimension to the repeal effort. Research from the Center for American Progress highlights that LGBTQ+ individuals of color face compounded discrimination, making representation in leadership roles particularly impactful. Jones' leadership on House Bill 1738 not only advances LGBTQ+ rights but also amplifies the voices of marginalized communities within the broader movement.
Jones' acknowledgment of standing "on the shoulders" of previous advocates reflects a deep awareness of the interconnected struggles for civil rights across racial, gender, and sexual orientation lines. This perspective enriches the repeal effort, positioning it as part of a larger fight for justice and equality.
Looking Ahead: The Path to Final Repeal
Challenges in the Senate
As House Bill 1738 moves to the Senate, it faces a formidable challenge. The Senate's more conservative composition and the looming end of the legislative session on June 2, 2025, create a narrow window for action. Advocates will need to navigate a crowded legislative agenda and persuade skeptical senators to prioritize the bill.
Strategies to secure Senate approval may include emphasizing the bipartisan support in the House and framing the repeal as a matter of legal consistency and individual liberty. Public pressure, driven by advocacy groups and media coverage, could also play a decisive role.
Long-Term Implications
Should the bill pass, it would mark a significant milestone in Texas' journey toward equality, sending a powerful message about the state's commitment to inclusivity. However, the repeal is just one step in addressing the broader challenges facing LGBTQ+ Texans, including discrimination in employment, housing, and healthcare.
Future legislative efforts may focus on enacting comprehensive nondiscrimination protections, strengthening hate crime laws, and supporting LGBTQ+ youth in schools. These initiatives would build on the momentum of the repeal, creating a more equitable and just Texas.
Conclusion: A Step Toward a More Inclusive Texas
The Texas House's vote to repeal the homosexual conduct ban is a historic achievement, reflecting decades of advocacy, shifting political dynamics, and a growing recognition of the need to align state law with constitutional protections. While the bill's fate in the Senate remains uncertain, its passage through the House is a testament to the power of perseverance, coalition-building, and principled leadership.
For Rep. Venton Jones and countless others, this effort is deeply personal, rooted in a desire to dismantle the vestiges of discrimination and affirm the dignity of all Texans. As Texas moves forward, the repeal of this outdated law serves as a beacon of hope, illuminating the path toward a more inclusive and equitable future.

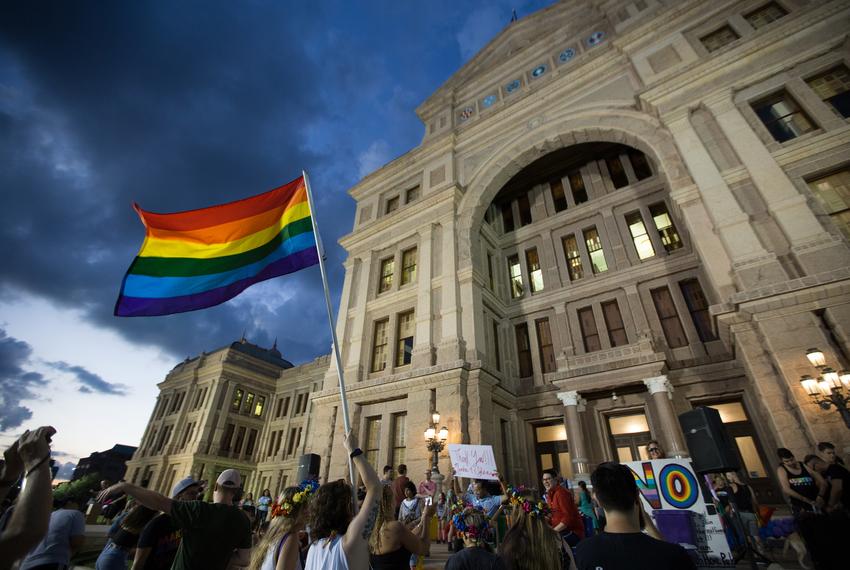


























0 Comments